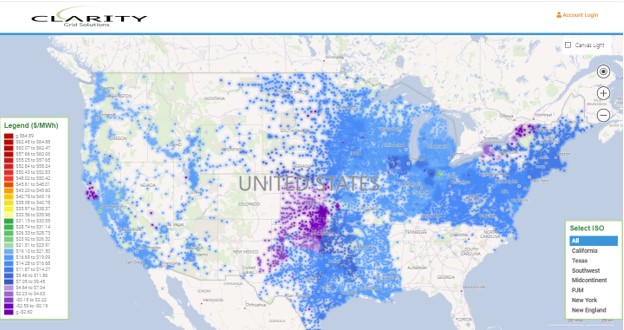
Executive Summary
SPP grew its nodal count during the Third Quarter 2022 almost exclusively through the addition of WAPA’s Western Area Colorado Missouri Balancing Area Utilities. The inclusion of nodal points owned by Basin Electric, Black Hills Electric, Cheyenne Light Fuel and Power, High West Energy, and Tri-State G&T, amongst others, added over 500 nodes not previously included in any ISO territory. In addition, over 4 gigawatts of generation and over 1 gigawatts of storage were added over the quarter, reversing the trend of minimal additions seen in 2Q 2022.
Much discussion is taking place regarding the slow response of regulatory authorities to entities seeking to respond to economic signals regarding absence of new generation or storage capacity, push to make the grid cleaner, and lately legislative initiatives creating new incentives for clean generation and energy storage. One indicator of the efficiency of various regional regulatory bodies have processed requests to build new generation and storage is the speed in which Interconnection Request have been approved. Some projects make their way through the siting and approval process, and some do not. However, one of the most significant phases for any new construction on the Grid is the assignment of a Price Node or PNode by the ISO regulatory authorities. This can indeed occur before any visual satellite evidence of the facility can be seen, or even prior to energy or services being taken from, or provided to the Grid. Still, this is an important designation in the life of the facility (substation or generation) indicating that a unique price for the value of energy is now being published as a result of the ISO SCED (Security Constrained Economic Dispatch) process which produces a Locational Marginal Price (LMP) for the physical location.
Clarity PNode Additions
Because the economic and physical structure can best be understood beginning at PNode layer, the current composition of the Load and Generation pricing and location is of great interest to a wide assortment of Grid Stakeholders, renewables developers, marketers and traders, DER developers, and even EV charging infrastructure developers. Therefore, we spend a great deal of effort at Clarity Grid mapping not only the existing set of grid elements but also adding those which appear on a continuing basis through the data feeds of each respective US ISO. Recently a major factor in PNode additions has been the inclusion of an entire Utility’s grid infrastructure as is becomes a member of an existing ISO. The most significant growth in nodal counts recently has been through the growth of CAISO’s Extended Energy Market. This quarter, however SPP’s newly created imbalance market Western Energy Imbalance Service (WEIS) led the charge in filling in new areas of the US West including Colorado, Nebraska, and Wyoming, https://spp.org/weis. SPP recently announced that WEIS Utilities would be transferred from the imbalance market to RTO West or Markets + Program, the market structure of which is unclear.
As can be seen from the Chart below, over the 3rd quarter of 2022 792 new nodal points were added to the Clarity platform, 701 Load and 91 Generation. The vast majority of new nodes were added in SPP due to the WEIS additions discussed above. Outside of SPP, ERCOT continued the momentum seen in previous quarters of adding the most significant number of Load nodes and all representing newly constructed substations, not the merging of previously non-ISO infrastructure, in this case 122 Load nodes. Conspicuous in the lack of activity was PJM which saw no new additions of either load or generation. Modest additions to MISO and CAISO rounded out the additions with 58 and 92 additions of both load and generation respectively.
| | CAISO | PJM | SPP | NYISO | NEISO | ERCOT | MISO | Total Fuel Type |
| B | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 21 |
| BM | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| C | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| H | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| N | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| NG | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| S | 23 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 37 |
| D | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| W | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 12 |
| Total ISO | 51 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 26 | 91 |
| CAISO | PJM | SPP | NYISO | NEISO | ERCOT | MISO | Total Load | |
| Load | 41 | 0 | 501 | 0 | 5 | 122 | 32 | 701 |
Newly Constructed Generation (Storage) by Fuel Type
If we drill down into the raw additions by node and examine actual capacity added to each system and segment by fuel type, we get a fuller picture of how grid capacity within the respective ISOs is changing. As shown below, over 4 gigawatts of generation was added to the grid as defined by new Pnode additions. Three quarters of this capacity was made up by solar and the remainder wind facilities. Regionally a large portion of solar additions occurred surprisingly in MISO while CAISO saw the greatest growth, followed by ERCOT. Over recent periods ERCOT has led all ISOs in additions of storage, and this was the case over the most recent quarter, however CAISO registered almost an equal level of growth of just over 50 megawatts.
| | NYISO | NEISO | PJM | MISO | SPP | ERCOT | CAISO | Totals |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Solar | 0.0 | 10.0 | 0.0 | 1189.0 | 0.0 | 502.3 | 1300.0 | 3001.3 |
| Hydro | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Natural Gas | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| BM | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Battery | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.0 | 0.0 | 537.0 | 507.0 | 1056.0 |
| Wind | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 871.0 | 0.0 | 300.0 | 0.0 | 1171.0 |
| Coal | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Distillate | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Generation | | | | | | | | 4172.3 |
| Storage | | | | | | | | 1056.0 |
Noteworthy Examples of Load Additions:
Taking a look at some specific load points (substations) coming on in the 3Q 2022:
MISO:
ETEC’s newly constructed Stryker 138 kv substation in Corrigan, TX built to serve TransCanada’s (PS 40) also newly constructed pumping station (visible just to the east).
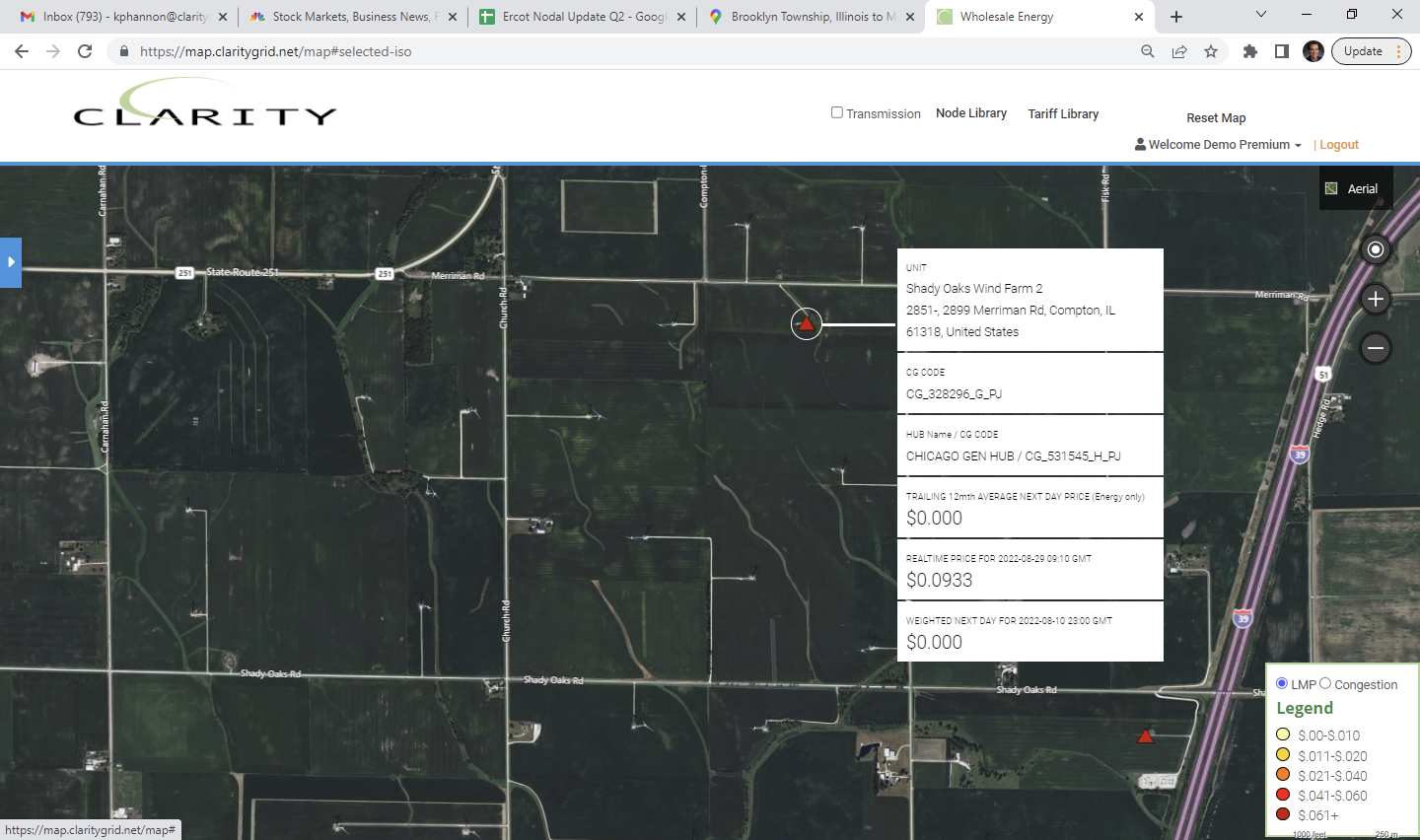
CAISO:
In CAISO EIM member APS territory Goodyear, AZ view of newly constructed 230 kv Stratus substation. This substation is located just southwest of Amazon’s new Robotics facility GYR2, the largest building to be constructed in Goodyear, AZ.
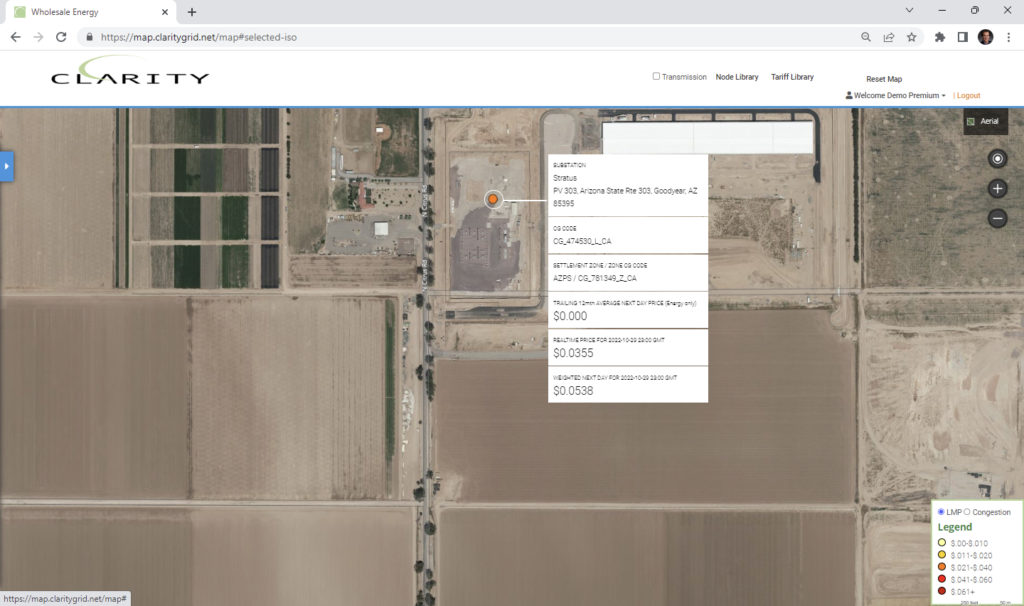
Noteworthy Examples of Generation Additions:
ERCOT:
El Sauz 300 mw Wind Farm constructed by JERA Americas located in Raymondville, TX.
NEISO:
Drybridge Solar in North Kingstown, RI a newly constructed 50 mw solar facility owned by Brown University and constructed by Constellation Energy and Energy Development Partners.
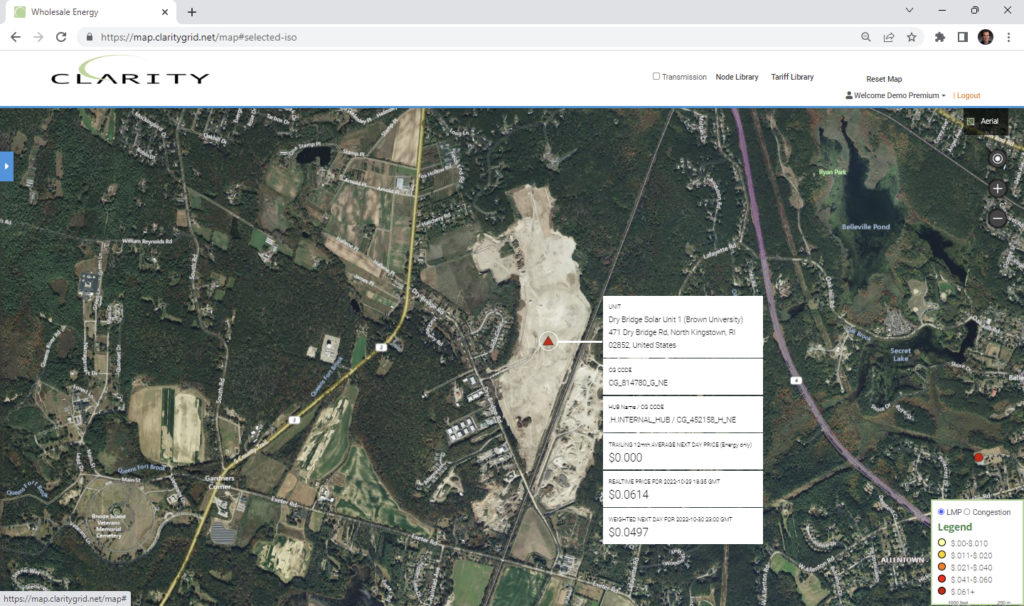
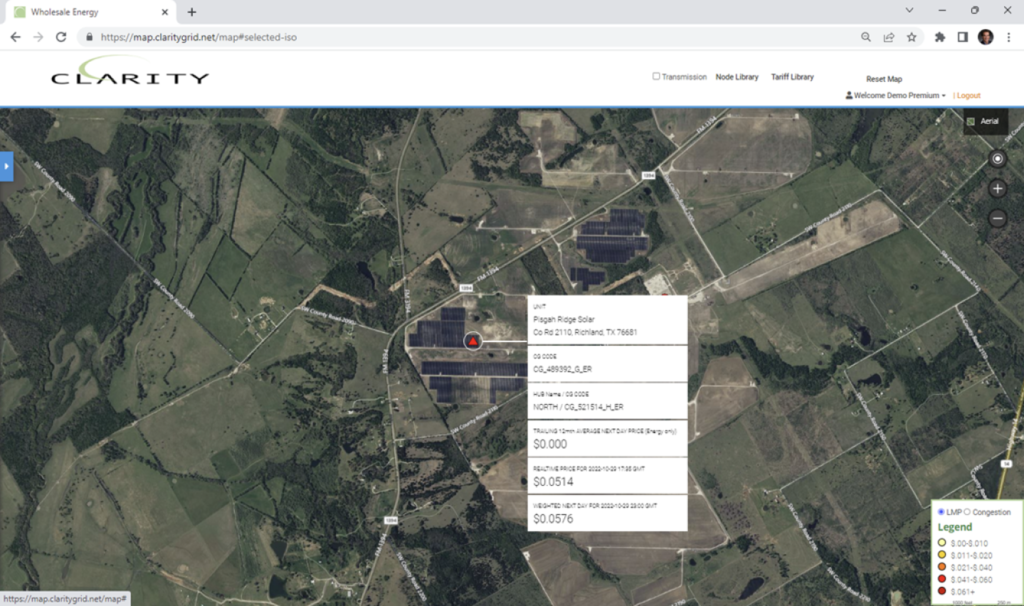
ERCOT
Pisgah Ridge Solar, Duke’s newly constructed 250 mw facility in Richland, TX.
Noteworthy Examples of Storage Additions:
MISO:
Deer Run Battery Storage is a 5-mw new battery facility in Cedar Rapids, IA owned by Alliant Energy.
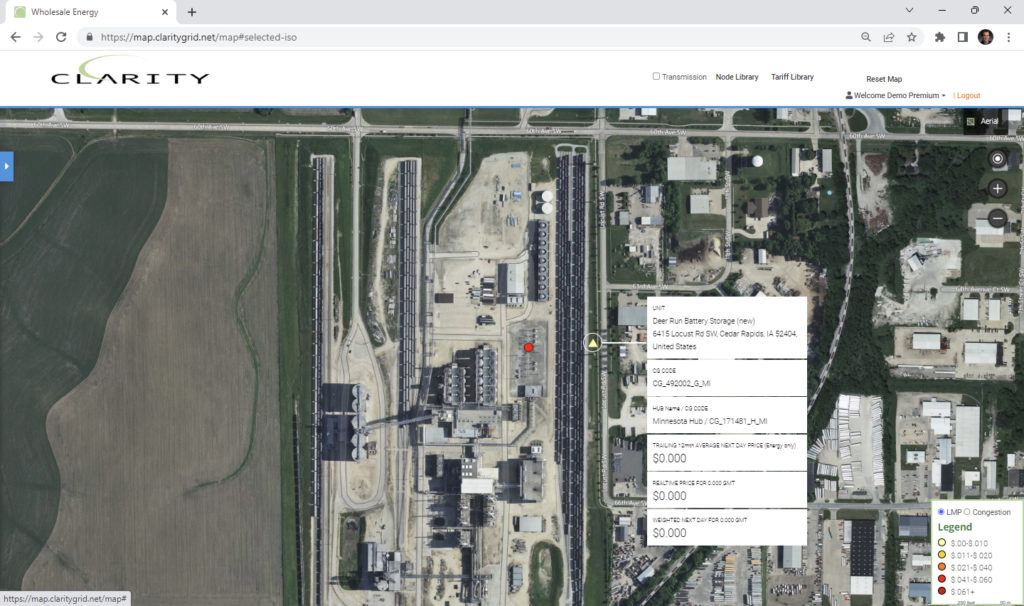
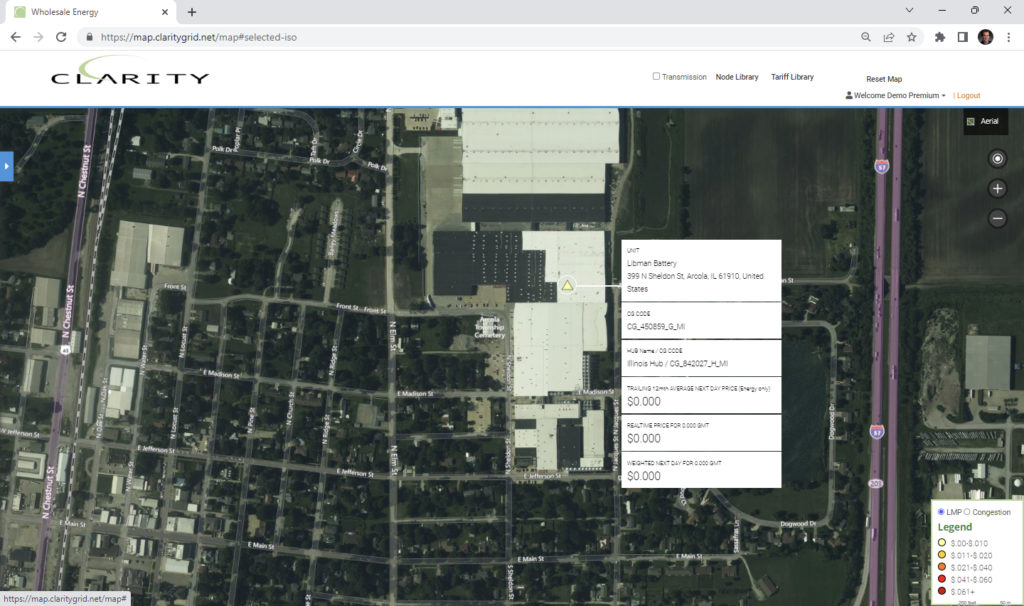
MISO:
The Libman 2 mw Battery facility is registered as a generation resource and is paired with a 1.8 mw solar facility providing resiliency for the Libman company in Arcola, IL.
CAISO:
The largest additions of storage in CAISO are due to pairings with two large solar facilities: Dagget Solar in Daggett, CA and Arlington Solar in Blythe, CA, the site of the Arlington. The Daggett storage facility has a stated capacity of 132mw/528 mwhr and is owned by NextEra Energy Resources.
If you are interested in viewing all existing and new load and gen facilities, please inquire about a trial at https://www.claritygrid.net and select “Request a Demo.”